Brad DeLong, as best I can tell, does not lead the Washington Center for Equitable growth. Along with Nick Bunker he does, however, produce many of their best blog posts (RSS icon proudly displayed) - like two from a Hamilton Project Future of Work conference (intro PDF, Brynjolfsson and McAfee [1]) that I recently posted back-to-back in my app.net feed.
The first is by Brad, taken from a Larry Summers speech which explains why Summers matters (emphases mine) …
Morning Must-Watch: Larry Summers and Friends: The Future of Work - Washington Center for Equitable Growth
… we have enormous antidotal evidence and visual evidence of [modern IT/AI] technology having huge and pervasive effects … On the other hand, the productivity statistics over the last dozen years are dismal. Any fully-satisfactory synthetic view has to reconcile those two observations…
… I think it is a mistake to think of the economy as homogeneous–as producing something called “output”. As we approach these issues, an aspect that doesn’t get enough attention is that sectors through progress work themselves into economic irrelevance. … candle-making was a major industry in the 1800s, illumination is a trivial industry today….
We need to recognize that a sector that has rapid technological progress but of which the world can absorb only so much becomes ultimately unimportant in the economy….
…Consider two goods today: a television set, and a year at a university (or I could use a day in a hospital). The consumer price index for the latter two categories is in the neighborhood of 600. the consumer price index for the former category is 6. There has been a hundredfold change in the relative price of TV sets and the provision of basic education and health care services.
If anybody is wondering why governments can’t afford to do the things they used to do, I just gave you a big hint.
If anybody’s wondering where most people are growing to be working in the future, i just gave you a big hint.
If anybody’s completely confident we will have rapid productivity growth in the future, they should be giving pause–because no matter how much productivity we have in agriculture or illumination, it doesn’t really matter for the aggregate economy. Increasingly, that’s becoming true of a larger and larger fraction of what it is that we produce.
… in the 1960s,= ,,, about 6% of the men in the United States between the age of 25 and 54 were not working. Today, 16% of the men in the United States between the age of 25 and 54 are not working. It won’t be very different even when the economy is at full employment.
Something very serious has happened with respect to the general availability of quality jobs in our society.
… Whether you think it is due to technology or to globalization or to the maldistribution of political power, something very serious is happening in our society.
The second is by Nick Bunker …
What to worry about on the supply side - Washington Center for Equitable Growth
… A new paper by economists Stephen G. Cecchetti of Brandeis International Business School and Enisse Kharroubi of the Bank of International Settlements argues that an over-bloated financial sector can reduce productivity. They contend that by drawing talented workers toward Wall Street, the finance sector lowers the total productivity rate….
From Summers we see that certain technologies have dramatically diminishing returns, so that they become a smaller part of a larger whole. Obvious, now that he’s pointed this out. There is only so much light that we can use. Is this also true of computing power? Is it true of energy?
Is Summers saying all employment will shift to expensive and inefficient health care and education? Isn’t that what Baumol said?
It’s a good exercise to consider how computational processing could follow the path of the lightbulb. There is, for me, no significant difference between a response time of milliseconds and picoseconds. Between modern processors and SSDs there seems no pressing need desktop performance increases. To some extent the human users is the rate limiting step. Only when one eliminates the human user does a millisecond vs. picosecond delay matter, as with high frequency stock “trading” (manipulation) — or the timescales of an AI.
Thinking of high frequency trading, we are reminded that vast amounts of modern economic activity transfer wealth without producing product. They have low to negative productivity, as found by Cecchetti and Kharroubi. Some of these are parasitic processes as would arise from any complex adaptive system, others are forms of more or less transparent fraud rooted in complexity exploitation. In our times information technology has been an essential enabler of both.
Considering failures of productivity enhancement, what do we make of Google Search? Ten years ago Google Search was miraculous, now it increasingly fails to produce much of value [2]. The web grew very quickly on an advertising based business model, but that model has failed and a new model is unborn. Progress is unpredictable in whitewater times.
Or consider email. We’ve been using it widely for almost 30 years, yet very few people use email well. Much time in routine corporate life is wasted by incompetent email [3]. Alas, email’s failures can’t compare to the disappointment of the “electronic health record” or “EHR”
Ahh, the EHR! What dreams we had in the 1980s. Dreams that took me from rural practice to another degree to a career in healthcare IT. It was so obvious how patients would benefit, and how all providers would become far more productive.
The reality of the EHR has been a crushing disappointment. One day, perhaps, the dreams will come true — but nobody in 1990 would consider the state of clinical automation in 2015 anything but an appalling failure. A failure not of technology, but of business incentives, of markets, and of complex interlocking rigidities.
The list goes on. The same technology that enables location-based alerts also enables malware and adware. Our economic landscape has been transformed; new technology causes vast wealth creation, but then wealth concentration drives the greater economy to a stagnant deflationary spiral.
Perhaps we’ve been here before. It took 60 years after the 1780 “start” of the industrial revolution for worker living standards to definitively rise. If our revolution started 70 years ago, maybe the rise will start any time now.
Or perhaps we’re headed in a different direction. An Economy is not a system for satisfying humans, or a system for producing goods or wealth or jobs. The “Complex Adaptive System” cliche truly applies. It is an immaterial ecosystem that produces things like wealth and jobs, but also emergent amoebacorp and brain sucking jobs in finance. The Economy is a beast of its own, slouching towards Bethlehem.
- fn -
[1] The PDF includes two killer graphs …
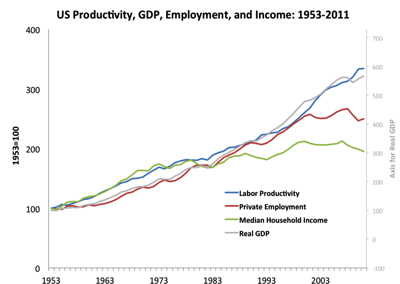
and

[2] While writing this post I often searched for prior posts in notes.kateva.org. Google did a poor job, Duck Duck Go constrained to “site:kateva.org” did much better.
[3] If you ever hear of a corporation that teaches employees to write effective email please let me know. I’d like to buy shares.
Related


